by Shelby Wyzykowski
In the classic 1953 movie “Gentlemen Prefer Blondes” is a memorable musical number performed by silver screen legend Marilyn Monroe. Wearing a striking pink satin gown and dripping in dazzling jewels, she is surrounded on the stage by a bevy of handsome suitors that are dressed to the nines. In this glamorous setting, she sings the praises of diamonds…how nothing in the world can compare to how it feels to possess these glittering gemstones. But off-screen, Monroe’s taste in brilliant baubles was radically different, preferring costume jewelry to the real thing. I have to admit that I agree with Marilyn. Diamonds have never held much interest for me. That is until now. After doing a little research, I’ve discovered that, besides their use in the jewelry industry, there are other ways in which diamonds are utilized in society today. In fact, there is so much more to these captivating stones than just their scintillating sparkle.
Perhaps you’ve heard the adage “one person’s trash is another person’s treasure.” Well, it just might surprise you that this saying holds true for diamonds. In the jewelry world, a diamond with perfect clarity is the much-desired ideal. But in the scientific world, a so-called “poor” specimen that is full of inclusions (imperfections), could hold a treasure trove of geologic information. Researchers are studying them to try and uncover the secrets of the deep-Earth environment. The majority of diamonds are created fairly close to the Earth’s surface, between 93 and 150 miles down. But there are some diamonds, called super-deep diamonds, that come from far down in the Earth’s mantle and are as deep as 500 to 600 miles (the mantle, which is mostly made up of solid and very hot rock, is directly below the Earth’s surface layer, or crust, and makes up more than 80 percent of our planet’s volume). These 3.5 billion-year-old gems formed at a pressure that is 240,000 times the atmospheric pressure at sea level, and this fact makes these tiny stone time capsules extremely valuable to researchers. No doubt geologists would love to travel deep under our planet’s surface like the characters in Jules Verne’s 1864 science fiction novel Journey to the Center of the Earth. Unfortunately they can’t, but these super-deep diamonds are the next best thing to journeying there themselves!
With these diamonds, scientists are uncovering clues to the origins of water on Earth. Did water come from incoming asteroids and comets, or was water an integral component at the planet’s formation? We’re still not quite sure. But diamond research has brought us closer to figuring out how much water lies deep underground. Scientists think that there may in fact be as much water present in our planet’s deep subsurface as there is found in our oceans. They have developed this idea after discovering a special water encased in the inclusions of deep diamonds. Called ICE-VII, this water ice can only be formed under tremendous deep-Earth pressure. In addition to water, geologists have found an elusive mineral in diamond inclusions. Scientists had theorized it to be an extremely common mineral that makes up to 38 percent of the Earth’s volume, but it’s been impossible to create in a lab. Now that it’s been found in nature, researchers have the proof of its existence and have named it Silicate-Perovskite (or Bridgmanite). In addition to Bridgmanite, they have discovered other trace minerals and elements that are commonly present in the Earth’s crust. This means that the materials were subducted (drawn back down into the Earth) billions of years ago by plate tectonics. Deep in the mantle, the materials were encased in a forming deep-diamond and then eventually sent back up to the surface by way of volcanic eruptions. Even more exciting than all of these discoveries is the thought of what geologists still have yet to uncover. They still hope to find carbon from primordial organic matter in these special diamonds. That matter could be a clue to the origins of life on Earth!

In addition to their contributions to the scientific field, diamonds also have practical uses in society. In the mid-1950’s, synthetic diamonds were invented. Created in a lab, they are chemically and physically exactly the same as natural diamonds. However, these man-made gems do not possess the allure and mystery of natural diamonds, so they are not very desirable in the jewelry market. But since diamonds are the hardest known natural substance, they are ideal for industrial use. For example, they can be pulverized into a fine abrasive that can be made into a “diamond paste” and used for polishing other jewelry-grade gemstones. Small particles of diamond can also be embedded in tools like saw blades, drill bits, and grinding wheels. These diamond-coated tools are very wear-resistant and can be used for mining, deep-sea drilling, and road construction. And there are some ingenious uses for diamonds that you may find to be very surprising. Diamond windows can be made from very thin (thinner than a human hair) diamond membranes. These windows cover X-ray machines, laser openings, and vacuum chambers. A diamond can also make your music sound better. A speaker dome made out of diamonds can vibrate very rapidly because this gem is such a stiff material. So it is ideal for enhancing the performance of high-quality speakers. Diamonds can even help you keep track of time. Small mechanical devices, such as watches, have tiny bearings inside of them that make everything move (in a watch, it’s called its “movement”). A thin coating of diamond makes these parts wear-resistant and ensures accurate time-telling and lasting durability. From helping to build highways to making your timepiece tick, who knew that diamonds could be so useful in so many ways!
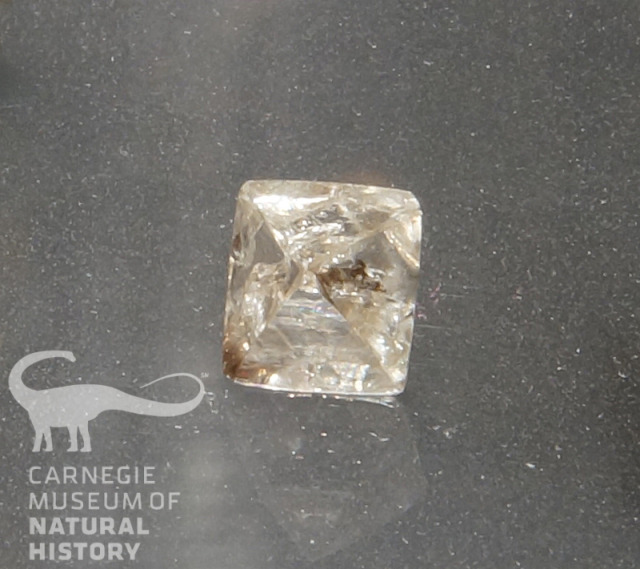

Yet another important role that diamonds have played in our world is how they have influenced history. The brilliantly blue, supposedly cursed Hope Diamond, for example, has not brought much luck to its owners since it was discovered over 350 years ago. It was in the possession of Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI until their untimely deaths during the French Revolution. Subsequent owners also met with unfortunate outcomes until it was donated to the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History where it is now safely on display. Another famous diamond, the 750 year-old Koh-i-Noor, has been owned by many royal rulers. It once decorated the Peacock Throne that was used by the Mughal Emperors of India, including Shah Juhan, the builder of the Taj Mahal. Now in England, the stone is part of the Imperial Crown. Due to an alleged curse, it can only ever be worn by the royal family’s female members. Finally, there is the Regent Diamond, which was unearthed in the early 1700’s. After being owned by several rulers, it disappeared during the French Revolution. Years later, it reappeared in the sword of Napoleon. But he was unable to hold onto it for long. After being defeated by the British in the Battle of Waterloo, the once-great ruler was exiled to the tiny island of Elba in disgrace. Since 1987, the Regent’s home has been at the French Royal Treasury in the Louvre in Paris. But you don’t need to travel to France or Great Britain or Washington D.C. to see the Regent Diamond, the Koh-i-Noor, and the Hope Diamond. Replicas of these three stones plus many more world-famous diamond replicas are on display at the Hillman Hall of Minerals and Gems. While you’re there, you can also admire some expertly crafted pieces of authentic diamond jewelry that would make any gem lover’s heart skip a beat.
Even though Hillman’s diamond collection is truly amazing, I can’t help but wonder if it would have impressed someone like Marilyn Monroe. Apart from a single piece of jewelry, the diamond wedding band that was given to her by Joe DiMaggio, she had no real affinity for diamonds. Apparently, the legendary actress didn’t believe that they’re a girl’s best friend. But if she had been given the opportunity to find out about all of the other meaningful ways in which diamonds benefit our world, perhaps this screen siren might have developed a new appreciation for these precious gems. I know that I have. I’d like to think that Marilyn would have too.
Shelby Wyzykowski is a Gallery Experience Presenter in CMNH’s Life Long Learning Department. Museum staff, volunteers, and interns are encouraged to blog about their unique experiences and knowledge gained from working at the museum.
Related Content
Wulfenite and Mimetite: CMNH’s Crystal Banquet
Rockin’ Minerals Coloring Pages
Ask a Scientist: Why do some minerals glow?
Carnegie Museum of Natural History Blog Citation Information
Blog author: Wyzykowski, ShelbyPublication date: June 23, 2021